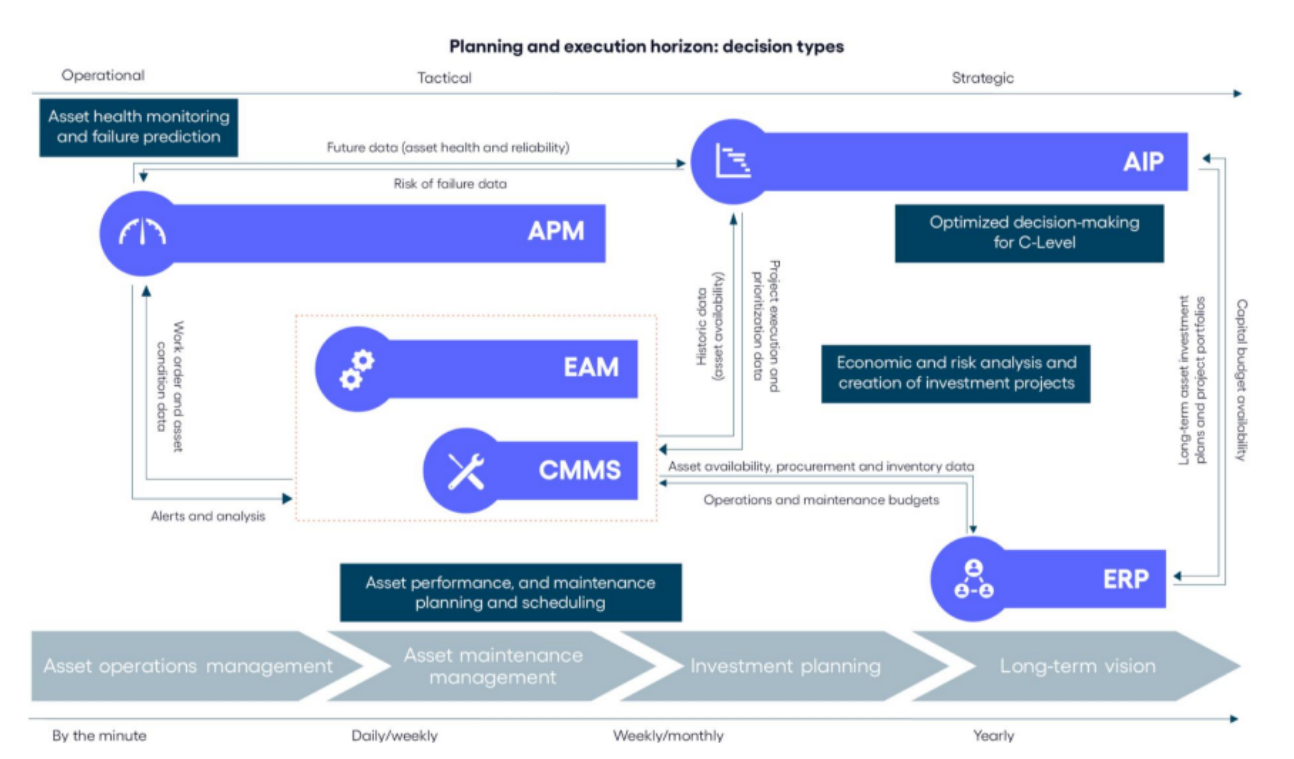
How does EAM integrate with Asset Investment Planning (AIP)?
When asset-intensive organizations integrate Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) with Asset Investment Planning (AIP), they can strategically align maintenance and investment decisions from the operational to strategic level.
What is Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)?
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) systems are typically used in asset-intensive industries like electric utilities and municipal governments to optimize the day-to-day operations. Work management, asset maintenance, planning and scheduling, supply chain management are just a few of the initiatives an organization would typically manage through their EAM.
Enterprise Asset Management systems leverage data analytics to extract insights from asset data. Once all asset data is centralized in an EAM, the system analyzes trends to indicate potential asset failures. With this information, organizations can schedule inspections or maintenance proactively, minimize downtime, reduce repair costs, and extend asset life overall.
Key components of EAM
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) encompasses vital components crucial for optimizing asset lifecycle management within organizations.
Key components include:
- Asset tracking
- Maintenance scheduling
- Inventory management
- Performance analytics
EAM systems ensure efficient utilization, minimize downtime, extend asset lifespan, and enhance productivity.
Importance of data analytics in EAM
Enterprise Asset Management systems leverage data analytics to extract insights from asset data, enhancing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By centralizing all asset data, EAM systems identify trends and patterns that indicate potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach allows organizations to schedule inspections and maintenance activities strategically, minimizing unplanned downtime, reducing repair costs, and extending the overall lifespan of assets.
Data analytics in EAM enables predictive maintenance strategies, optimizing asset performance and reliability. By harnessing advanced analytics techniques, such as predict modeling and machine learning, EAM systems empower organizations to make informed decisions based on real-time data. This capability not only improves asset utilization but also supports sustainable growth and operational excellence in industries ranging from manufacturing and healthcare to utilities and transportation.
Benefits of implementing EAM systems
Implementing Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) systems offers numerous benefits to asset-intensive organizations.
EAM systems streamline asset lifecycle management by centralizing data, enabling efficient tracking, maintenance scheduling, and inventory management. This centralized approach enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and lowers maintenance costs.
Furthermore, EAM systems facilitate informed decision-making through data analytics, predicting potential asset failures and optimizing maintenance strategies. By improving asset utilization and reliability, organizations can achieve higher productivity, compliance with industry regulations, and overall cost savings. Implementing robust EAM solutions is essential for businesses looking to maximize their ROI and maintain competitive advantage in today’s dynamic market landscape.
What is Asset Investment Planning
Asset Investment Planning (AIP) differs from EAM largely in its scope. Where Enterprise Asset Management supports day-to-day operations, AIP supports long-term, strategic decisions typically pertaining to budget allocation and overall asset planning.
Leveraging asset data and models in AIP
Testing and comparing alternative strategies with AIP
From these initial results, organizations can begin testing and comparing alternative strategies. For example, if an electric utility wants to reduce their wildfire risk by 10% over the next five years, they can test investment scenarios like:
- Prioritizing the replacement of high-risk assets
- Investing in more vegetation management
- Investing in more frequent inspections
With Asset Investment Planning, the long-term feasibility and sustainability of investment decisions can be assessed and adapted in a repeatable, streamlined manner.
What are the benefits of integrating EAM with AIP?
Integrating Enterprise Asset Management with Asset Investment Planning allows asset-intensive organizations to collect and combine data from their assets, finance, regulatory, and operations to unlock financial returns and risk mitigations across the asset lifecycle.
Cities, government agencies, utilities, and transportation can leverage benefits like:
Align Investment with Asset Health
Asset-centric, data-driven decisions replace assumptions ensuring that investments are allocated to areas with the highest potential return at the right time, for the right amount.
Optimize Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance must continuously improve to remain effective as asset performance trends change. Testing asset intervention strategies in the AIP based on EAM data ensures the predictive maintenance remains effective.
Maximize Capital Allocation
Aligning investment decisions with asset lifecycles and performance metrics enables organizations to maximize asset value while minimizing operational costs and long-term financial risks.
Streamline Risk Management
Organizations can evaluate the financial and operational risk of their physical assets alongside investment risks. This holistic approach to risk management empowers decision-makers to implement proactive strategies that safeguard asset value.
What strategies can enhance the integration of EAM with AIP?
Though there are many benefits to be reaped from integrating EAM with AIP, anyone with experience integrating new technology into their stack can attest to the fact that it can be a complicated process.
But with these strategies in mind, organizations can greatly streamline the integration process to start creating the alignment between operations and strategy.
Establish clear goals and objectives
Firstly, organizations should establish clear goals and objectives for the integration, aligning EAM and AIP initiatives with strategic priorities. This ensures that integration efforts contribute directly to achieving to long-term financial and operational goals.
Implement robust data governance practices
The effectiveness of both EAM and AIP systems depend on quality data. Implementing robust data governance practices is essential to managing data quality, consistency, and security throughout the integration process and beyond. Organizations should invest in establishing data standards, protocols, and validation procedures to ensure the data drawn and generated by the EAM contributes to the best insight from the AIP and vice versa.
This enhances decision-making accuracy and minimizes risks associated with data discrepancies.
Foster cross-functional collaboration
Because AIP solutions can consider every aspect of an organization, spanning operations, finance, risk, and more, encouraging open communication and knowledge sharing facilitates the implementation and integration.
Getting stakeholders from different departments to contribute their expertise to optimize asset management and financial planning processes is key to a successful integration.
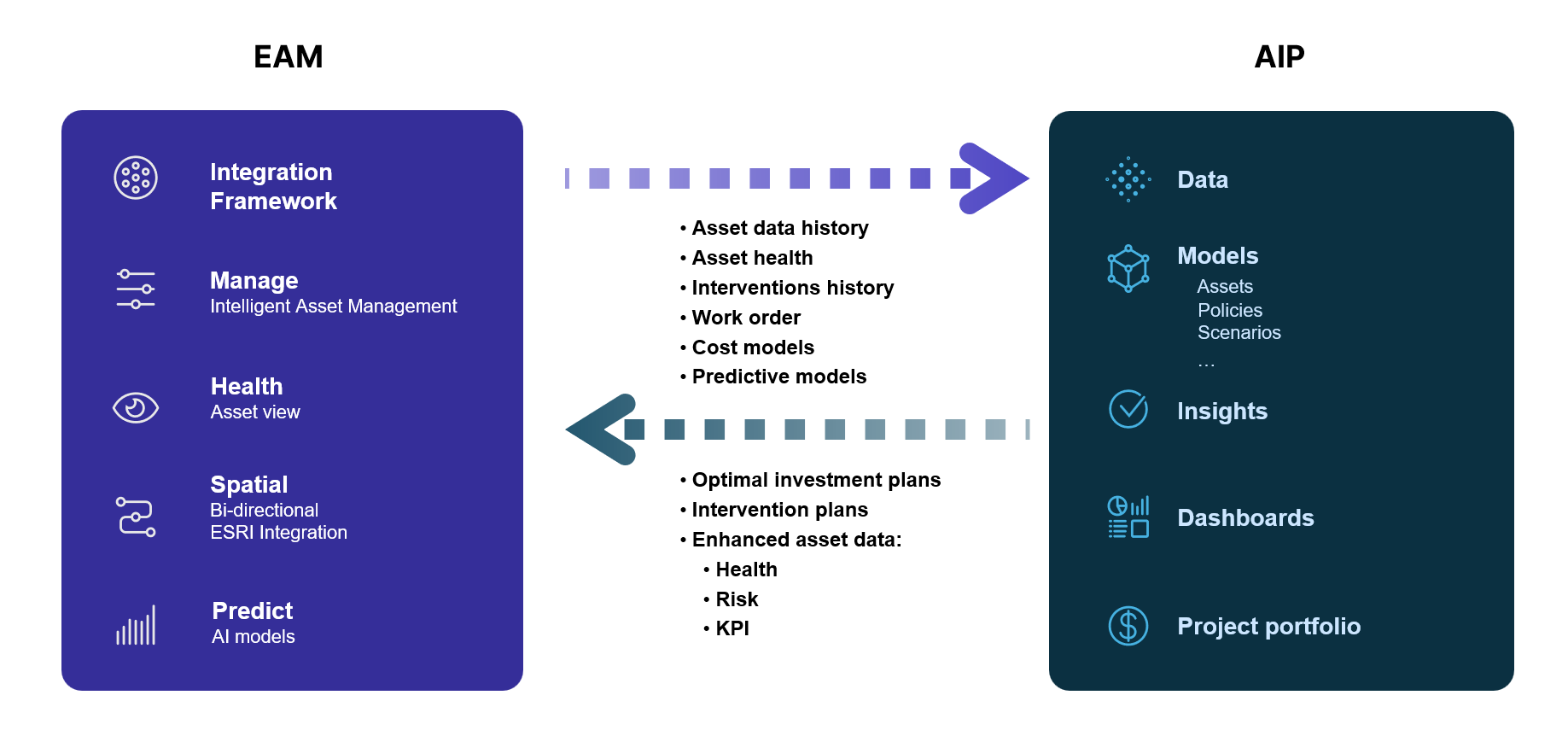
Integrating your Enterprise Asset Management with Asset Investment Planning
Understanding the Complexity of the Asset Management Ecosystem
The asset management ecosystem is complex, with new acronyms emerging regularly. However, integrating your Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) system with an Asset Investment Planning (AIP) solution like Direxyon’s can deliver substantial value to your organization. By leveraging comprehensive data integration and predictive analytics, this synergy optimizes resource allocation and enhances long-term strategic decision-making.
Explore the Benefits of Asset Investment Planning (AIP)
If you want to delve deeper into how Asset Investment Planning (AIP) can expand the scope and scale of your asset management strategy, you can read our detailed article on the tangible benefits and strategic advantages AIP offers. Discover how AIP aligns investments with asset health, enhances predictive maintenance strategies, and maximizes capital allocation for sustainable growth and operational efficiency.
Integrating your EAM with Direxyon
To learn more about how to integrate your EAM with Direxyon’s AIP and unlock its full potential for your organization, feel free to contact us today.
Our experts are ready to discuss your specific needs and provide tailored solutions that optimize your asset management processes.
FAQ: Integrating EAM with AIP
Enterprise Asset Management is asset management software used to manage the lifecycle of an organization's assets and reduce downtime. Helping to manage operational functions like work management, asset maintenance, planning and scheduling, and supply chain management, the real-time data these systems are essential for enhancing day-to-day efficiency.
Asset Investment Planning (AIP) involves the strategic planning and management of investments in an organization's assets and investments long-term. Through predictive modeling and simulation, AIP generates investment scenarios to determine best strategic allocation of capital and operational expenditures to ensure long-term sustainability.
Though both a part of the asset management software ecosystem, there a significant differences between EAM and AIP systems.
First, EAM tends to focus more on the enhancing the day-to-day efficiency of an organization. Meanwhile, AIP enhances the year-to-year sustainability of an organization.
Second, while EAM solutions can help organizations save money by extending asset life and reducing downtime, they typically don't have tools to conduct the complex, long-term financial modeling that is a hallmark of an AIP solution.
EAM and AIP work together by leveraging EAM data on asset performance, maintenance needs, and lifecycle stages to inform AIP strategies. AIP, in turn, uses this information to prioritize investments, interventions, budget allocations, etc.
With the optimal investment plan generated by the AIP, the EAM can recommend asset performance and maintenance needs in alignment to the overarching strategy.
This collaboration results in more informed decision-making, better resource utilization, and improved overall asset performance.